Both WPA/WPA2 personal and enterprise have the way to derive the source key - Pairwise Master Key or PMK. In case of WPA/WPA2 enterprise MSK(Master Session Key) is derived from EAP exchange and PSK is derived from MSK.1
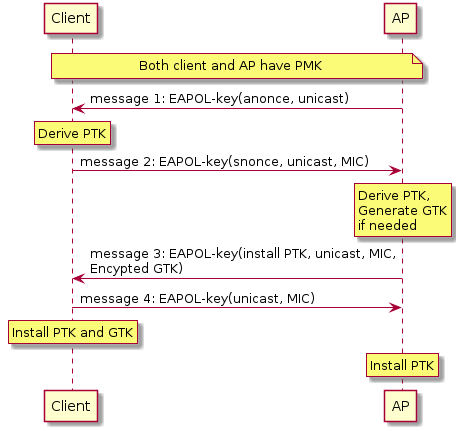
- AP sends EAPOL-key which contans anonce (AP or Athenticator nonce), which is a random value that prevents replay attacks. At this point, the client can derive PSK from PMK, MAC address of the client and AP, and two nonces.
- The cient sends a message that has snonce and MIC. The AP extracts the snonce and calculates PTK.
- Keys are now in place on both sides, but needs to be confirmed. The AP sends the client a message indicating the pairwise key will be added. It also includes the current group transient key to enable udpate of the group key.
- The client sends a final confirmation message to the AP.2
Glossary:
- ANonce : AP nonce
- EAP : Extensible Authentication Protocol. A framework authentication protocol used by 802.1X to provide network authentication. Authentication itself is delegated to sub-protocols called methods
- GTK : Group Transient Key. Derived from the GMK by combining with the group random number, the GTK is used to derive the group key hierachy, which includes keys used to protect broadcast and multicast data.
- MIC : Message Integray Code. A hash value caluated over a set of protected data to guard against tampering. In most cryptographic systems, such a hash is called a Message Authentication Code (MAC). 802.11 uses the algorithm MIC to avoid confusion with the Medium Access Control layer.
- PTK : Pairwise Transient Key. Ke derived from PMK that includes keys used by encryption and integrity protocols, but also includes keys to distribute dynamic keys.
- SNonce : STA nonce